Proper HVAC system sizing is crucial to ensuring comfort, efficiency, and long-term savings in your home or business. Knowing how to size a heating and air conditioning system correctly ensures that your system operates at its full potential.
Whether you’re a homeowner, builder, or DIY planner, this HVAC sizing guide will walk you through the key factors and steps in choosing the right size system for your space.
Why HVAC Sizing Matters
The size of your heating and cooling system sizing directly affects both the performance and efficiency of your HVAC system.
A system that is too small will struggle to heat or cool your space effectively, leading to discomfort and higher energy bills.
On the other hand, an oversized system may cycle on and off too frequently, leading to wear and tear, reduced efficiency, and higher upfront costs. Proper sizing helps ensure that your HVAC system runs efficiently, maintains comfort, and saves on energy.
Heating vs Cooling Load
The heating load refers to the amount of heat required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature in winter, while the cooling load refers to the amount of cooling required in summer.
These loads depend on various factors such as climate, insulation, and the design of your home or building.
In general, heating load is influenced by the home’s insulation, windows, and external temperature, while cooling load is affected by factors like solar gain, ventilation, and humidity.
Oversized vs Undersized Systems
If your system is too small, it will work harder to keep your space comfortable, leading to constant strain on the system, higher energy bills, and more frequent breakdowns.
On the other hand, an oversized HVAC system will cool or heat your home too quickly, resulting in short cycling.
Short cycling can cause higher energy usage, increased wear and tear, and inadequate humidity control. Therefore, it’s important to balance the heating and cooling load with the system’s capacity to ensure optimal performance.
A well-sized system will also maintain better humidity levels and provide consistent temperature control without overworking the equipment.
Manual J
For accurate HVAC system sizing, the Manual J calculation is the gold standard. This method takes into account the size, layout, and construction of your home to calculate the appropriate system size.
Manual J is often recommended or required by HVAC professionals to ensure accurate sizing and energy-efficient operation. It’s the key to making sure you don’t oversize or undersize your heating and cooling systems.
Who This Guide Is For
This guide is designed for:
- Homeowners who want to ensure they choose the right HVAC system for their home’s heating and cooling needs.
- Builders who need to consider proper sizing during the design and construction phase.
- DIY planners who want to calculate the correct size system before installation.
What Happens If HVAC is Sized Wrong
- Too small: System struggles to maintain temperature, leading to high energy bills and frequent breakdowns.
- Too large: System short cycles, wasting energy and reducing system lifespan.
- Inconsistent comfort: Difficulty in maintaining a steady temperature across the home.
- Higher costs: Increased installation and operational costs, especially with oversized systems.
Overview of Factors Affecting HVAC Size
| Factor | Impact on Size |
|---|---|
| Home Size and Layout | Larger spaces or multiple stories need a larger system. |
| Insulation | Better insulation reduces the heating and cooling load, allowing for a smaller system. |
| Windows | More windows, especially south-facing, increase cooling load. |
| Climate | Colder or hotter climates require more heating or cooling capacity. |
| Air Leaks | Unsealed gaps and leaks increase the heating and cooling load. |
| Occupancy | More people and appliances generate more heat, increasing the load. |
By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that your HVAC system is properly sized, providing comfort and efficiency. Remember, how to size a heating and air conditioning system is about balancing your home’s specific needs with the system’s capabilities.
Why Proper HVAC Sizing Is Critical

HVAC sizing importance cannot be overstated when it comes to ensuring your home or business stays comfortable and energy-efficient.
The right-sized system ensures optimal HVAC efficiency while preventing common issues like short cycling, high energy bills, and inconsistent temperatures.
Improperly sized systems, whether oversized or undersized, can cause unnecessary strain, increased costs, and even reduce the lifespan of your equipment.
Understanding HVAC sizing importance helps you choose the right system that meets your needs without overburdening your wallet.
Problems With Oversized HVAC Systems
An oversized HVAC system can seem like a good idea because it can heat or cool your home quickly. However, it leads to a host of problems that affect both comfort and efficiency:
- Short Cycling: An oversized system cools or heats the space too quickly, causing the system to turn off before it completes a full cycle. This constant on-off cycling leads to inefficiency.
- Poor Humidity Control: An oversized system doesn’t run long enough to remove sufficient moisture from the air, leading to higher humidity levels.
- Higher Energy Bills: Frequent cycling wastes energy, leading to increased utility bills.
- Shorter Equipment Lifespan: The system’s frequent cycling and overuse of power can lead to premature wear and tear, reducing the lifespan of the equipment.
Problems With Undersized HVAC Systems
On the other hand, undersized HVAC systems can struggle to maintain comfortable temperatures and run constantly, leading to several issues:
- Constant Running: An undersized system works harder to maintain the desired temperature, leading to continuous operation and excessive energy consumption.
- Inconsistent Temperatures: Due to the system’s inability to heat or cool the space adequately, certain rooms may be too hot or too cold.
- Higher Wear and Tear: Constant operation puts excessive strain on the system, leading to more frequent breakdowns and expensive repairs.
Comparison Table: Oversized vs Undersized HVAC
| Issue | Oversized HVAC | Undersized HVAC |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Wastes energy due to frequent short cycling. | Inefficient, constantly runs to maintain temperature. |
| Temperature Consistency | Poor temperature control, with uneven cooling/heating. | Inconsistent temperatures, with hot and cold spots. |
| Humidity Control | Poor humidity regulation, leading to discomfort. | Struggles to dehumidify, making it feel clammy. |
| System Lifespan | Shortened equipment life due to overuse. | Frequent wear and tear, leading to premature failure. |
| Utility Bills | Higher energy bills due to constant cycling. | High energy costs due to constant operation. |
Proper HVAC sizing ensures both comfort and efficiency. Whether you are dealing with an oversized or undersized HVAC system, each scenario comes with its own set of problems that can cost you more money in energy bills, repairs, and system replacements.
By choosing the right size system based on your home’s specific needs, you can avoid these issues and enjoy long-term energy savings.
Proper HVAC efficiency is all about finding the balance between too much and too little capacity. A well-sized system delivers maximum performance, comfort, and efficiency.
Factors That Determine HVAC System Size
When it comes to choosing the right HVAC system for your home or business, HVAC sizing factors are crucial to ensuring that your system runs efficiently and provides optimal comfort.
Proper heating and cooling load calculation is necessary to determine the size of the unit that will best meet the needs of your space.
Several variables influence the sizing process, and understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions when installing a new HVAC system.
Home Size and Square Footage
While home size and square footage are significant factors in determining the size of your HVAC system, they can be misleading on their own. Simply knowing the square footage doesn’t tell the whole story.
- Why Square Footage Alone Is Misleading: Square footage is just one factor in determining your system’s capacity. The number of rooms, ceiling height, and layout also play important roles.
- Open Floor Plans vs Segmented Homes: Homes with open floor plans may need a larger HVAC system to circulate air effectively through the entire space. In contrast, segmented homes with walls may trap air and create pockets of hot or cold spots, requiring a more precise heating and cooling load calculation for each zone.
Climate and Geographic Location
Climate plays a major role in determining the appropriate HVAC system size. The more extreme the climate, the larger the system typically needs to be.
- Hot vs Cold Climates: Homes in hot climates need a cooling system that can handle high temperatures for extended periods, while homes in colder climates need a system that can heat effectively during long winters. HVAC sizing factors will vary based on whether the system is primarily used for heating or cooling.
- Humidity Impact: High humidity levels in certain areas (like the coastal regions) mean the HVAC system needs to dehumidify the air, not just cool it. A larger system may be necessary to control humidity efficiently in these areas.
Insulation and Air Sealing
The quality of insulation and air sealing in your home is a key determinant of your HVAC system size. Proper insulation keeps the home warm in the winter and cool in the summer, reducing the load on your system.
- Attic, Wall, and Window Insulation: Homes with proper attic and wall insulation, as well as high-quality windows, reduce the load on your HVAC system. Poor insulation, on the other hand, requires more energy to maintain the desired temperature.
- Air Leakage Impact: Air leaks from cracks and gaps in doors, windows, and walls can reduce the effectiveness of your HVAC system. Proper air sealing reduces the system’s workload and may allow for a smaller system.
Windows, Doors, and Sun Exposure
The number and type of windows and doors, as well as the home’s sun exposure, also influence HVAC sizing. These factors affect both heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter.
- Orientation Matters: Homes that face the sun for most of the day experience higher heat gain. A home with a lot of windows facing the south or west may require a larger air conditioning system to counteract the extra heat entering the home.
- Single vs Double-Pane Windows: Homes with single-pane windows lose more heat in the winter and gain more heat in the summer. Double-pane windows are more energy-efficient and may allow for a smaller system, as they help maintain the interior temperature.
What Happens if HVAC is Sized Incorrectly
- Oversized System: Short cycling, poor humidity control, and higher energy bills.
- Undersized System: Constant running, inconsistent temperatures, and higher wear and tear.
Factor vs Impact on HVAC Size
| Factor | Impact on HVAC Size |
|---|---|
| Home Size and Square Footage | Larger spaces require larger systems to distribute heat/air. |
| Climate and Location | Hotter or colder climates require higher capacity systems. |
| Insulation | Poor insulation increases system size due to heat loss/gain. |
| Windows and Doors | More or larger windows increase the need for cooling/heating. |
The right heating and cooling load calculation is essential for determining the size of your HVAC system. Understanding HVAC sizing factors, such as your home’s size, insulation, climate, and window types, will help you choose the most efficient system for your needs.
A well-sized HVAC system not only ensures comfort but also saves energy and reduces operational costs over time.
Whether you’re a homeowner, builder, or DIY planner, taking these factors into account will ensure your HVAC system provides maximum efficiency and long-term reliability.
Understanding HVAC Sizing Measurements
When selecting an HVAC system, it’s essential to understand key sizing metrics such as HVAC sizing BTU, HVAC tonnage, and capacity requirements.
These measurements help ensure that the system you choose is appropriate for your home’s heating and cooling needs.
In this guide, we’ll explain how many tons HVAC do I need and clarify the concepts of BTUs and tons in the context of HVAC system sizing.
What Are BTUs in HVAC?
BTUs (British Thermal Units) are the standard unit of measurement for energy, specifically used to quantify the amount of heat required to raise or lower the temperature of a substance. In the context of HVAC systems, BTUs represent the heating or cooling power of a unit.
- Heating BTUs: When used in heating, BTUs represent the amount of energy a heating system, such as a furnace, uses to heat the air.
- Cooling BTUs: In cooling, HVAC sizing BTU indicates the amount of cooling power a system, like an air conditioner, provides to maintain a desired indoor temperature.
Understanding the correct HVAC sizing BTU for your space is critical to ensuring the system performs effectively and efficiently.
What Does “Tons” Mean in Air Conditioning?
When it comes to air conditioning, “tons” refer to the cooling capacity of the system. One ton of air conditioning equals the ability to cool 12,000 BTUs of heat per hour. This metric is commonly used in residential HVAC sizing to describe the system’s cooling capacity.
- 1 Ton = 12,000 BTUs: This is a standard conversion, meaning a 1-ton air conditioner can remove 12,000 BTUs of heat from a space each hour.
- Common Residential Tonnage:
- 1.5 to 2 tons: Suitable for small homes or apartments.
- 2.5 to 3 tons: Ideal for medium-sized homes.
- 4 tons or more: Used for larger homes with more square footage.
Example: If you live in a 1,500-square-foot home in a moderate climate, you might need a 2.5-ton system to properly cool the space. This system will remove 30,000 BTUs of heat per hour, ensuring your home stays cool and comfortable.
Typical HVAC Size Ranges for Homes
The size of the HVAC system required for your home depends on factors like the square footage, insulation, and climate. Here’s a breakdown of typical HVAC tonnage for various home sizes:
- Small Homes (1,000 to 1,500 sq ft): Typically, a 1.5 to 2-ton unit will suffice, providing adequate heating and cooling for smaller spaces.
- Medium Homes (1,500 to 2,500 sq ft): Homes in this range generally require a 2.5 to 3-ton unit for efficient temperature control.
- Large Homes (2,500 sq ft and up): Larger homes, especially in warmer climates, may need 4 tons or more of cooling capacity to ensure effective air conditioning.
BTU-to-Ton Conversion Table
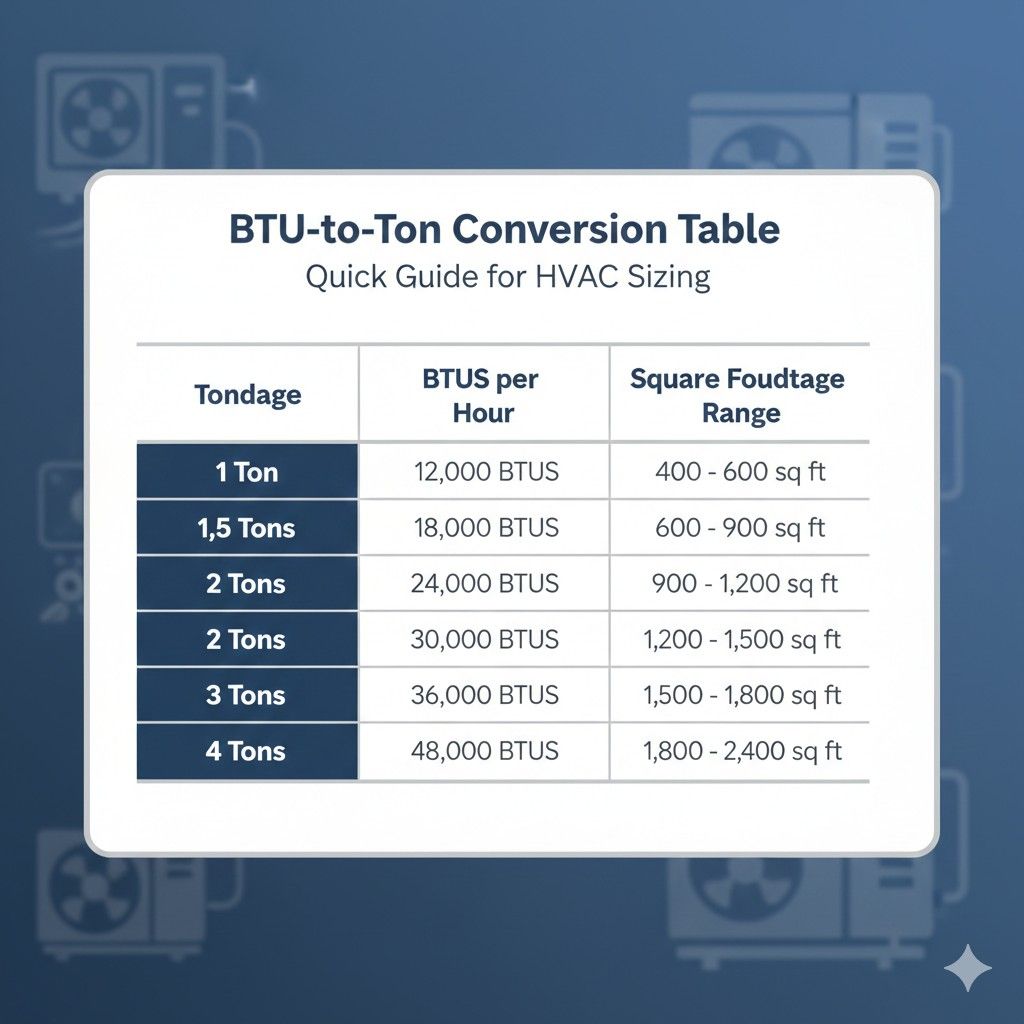
| Tonnage | BTUs per Hour | Square Footage Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Ton | 12,000 BTUs | 400 – 600 sq ft |
| 1.5 Tons | 18,000 BTUs | 600 – 900 sq ft |
| 2 Tons | 24,000 BTUs | 900 – 1,200 sq ft |
| 2.5 Tons | 30,000 BTUs | 1,200 – 1,500 sq ft |
| 3 Tons | 36,000 BTUs | 1,500 – 1,800 sq ft |
| 4 Tons | 48,000 BTUs | 1,800 – 2,400 sq ft |
Example Calculations
- Small Home (1,200 sq ft): For a home of this size, you would typically need a 2-ton system. This provides 24,000 BTUs of cooling per hour, which should effectively maintain the home’s temperature.
- Medium Home (2,000 sq ft): A 3-ton system would be required to meet the 36,000 BTU/hr cooling load, ensuring efficient temperature regulation in all rooms.
Understanding HVAC sizing factors like BTUs and tonnage is essential to ensure you choose the right system for your home.
Whether you’re determining how many tons HVAC do I need or conducting a heating and cooling load calculation, the goal is to select a system that provides optimal performance without overburdening your energy costs.
By understanding the HVAC sizing importance, you can ensure comfort, efficiency, and savings.
How to Size a Heating and Air Conditioning System Step-by-Step
Sizing your HVAC system correctly is crucial for ensuring energy efficiency, comfort, and cost savings. Incorrect HVAC sizing calculation can result in higher utility bills, uncomfortable indoor temperatures, and unnecessary wear on your equipment.
This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of how to size HVAC system correctly, making sure you choose the right system for your home.
Step 1 – Measure Square Footage
The first step in how to calculate HVAC size is determining the square footage of your conditioned space. This means measuring the areas of your home or building that will be heated or cooled. Do not include unconditioned spaces such as attics, basements, or garages in this calculation.
- Tip: Measure the length and width of each room and multiply to find the area. Add the square footage of each room to determine the total. Example:
- Living room: 15 ft x 20 ft = 300 sq ft
- Bedroom: 12 ft x 14 ft = 168 sq ft
- Kitchen: 10 ft x 12 ft = 120 sq ft
- Total conditioned space = 588 sq ft
Step 2 – Adjust for Climate Zone
Climate plays a significant role in HVAC sizing. Warmer or colder climates require larger systems to maintain comfort. Use regional multipliers to adjust for your area’s typical heating and cooling needs.
For example, homes in colder climates will need larger heating capacity, while homes in hotter regions will need more cooling power.
- Tip: The U.S. Department of Energy provides climate zone maps that can help you determine the appropriate multiplier for your region.
- Example: If your climate zone requires a 1.2 multiplier for cooling, and your home is 1,000 sq ft, you would multiply the area by 1.2 to adjust for the climate.
Step 3 – Account for Insulation and Windows
The quality of your home’s insulation and windows affects how well it retains heat or cold. Well-insulated homes require a smaller HVAC system, as they are more energy-efficient.
Conversely, homes with poor insulation or inefficient windows may require larger systems to compensate for heat loss or gain.
- Tip: Adjust your HVAC sizing calculation based on the quality of insulation, the number of windows, and their efficiency (e.g., double-glazed vs. single-pane). Example: If your home has excellent insulation, use a lower multiplier (e.g., 0.9). If it has poor insulation, you may need to increase the multiplier (e.g., 1.2).
Step 4 – Calculate Heating and Cooling Loads
To size an HVAC system, you need to calculate the heating and cooling loads. This step involves determining how much heating or cooling is required to maintain the desired temperature in your space.
A common method for this calculation is the Manual J load calculation, which takes into account factors like insulation, window type, climate, and square footage.
- Tip: Professional HVAC technicians typically perform this step using specialized software to calculate the load accurately. Example: A typical 1,000 sq ft home in a moderate climate may need 30,000 BTUs for heating and 24,000 BTUs for cooling.
Step 5 – Convert BTUs to HVAC System Size
Finally, after calculating the heating and cooling loads, you’ll convert these values into the appropriate system size. HVAC systems are often sized in tons (1 ton = 12,000 BTUs). To convert BTUs into tons, divide the total BTU requirement by 12,000.
- Tip: If the heating load is 36,000 BTUs and the cooling load is 24,000 BTUs, divide each value by 12,000 to get the system size in tons. Example:
- Heating Load: 36,000 BTUs ÷ 12,000 = 3 tons
- Cooling Load: 24,000 BTUs ÷ 12,000 = 2 tons
This means you would need a 3-ton heating system and a 2-ton cooling system.
Worked Example Table
| Factor | Heating Load (BTUs) | Cooling Load (BTUs) | System Size (Tons) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Size | 1,000 sq ft | 1,000 sq ft | |
| Climate Zone Adjustment | 1.2 (cooling) | 1.2 (heating) | |
| Insulation/Windows Adjustment | 0.9 (good insulation) | 0.9 (good insulation) | |
| Adjusted Heating Load | 36,000 | ||
| Adjusted Cooling Load | 24,000 | ||
| Heating System Size (Tons) | 36,000 ÷ 12,000 = 3 tons | 3 tons | |
| Cooling System Size (Tons) | 24,000 ÷ 12,000 = 2 tons | 2 tons |
HVAC sizing is an essential step in ensuring your heating and cooling systems are both efficient and effective.
By following this step-by-step HVAC sizing guide, you can calculate the proper heating and cooling loads, determine system sizes, and ensure that your new HVAC system is properly sized to meet your needs.
Whether you’re a homeowner, builder, or DIY planner, understanding how to calculate HVAC size will help you make informed decisions that save energy, reduce costs, and enhance comfort in your space.
Manual J Load Calculation Explained
A Manual J HVAC calculation is the industry standard used to determine the appropriate size of a heating and cooling system for a specific building.
This calculation ensures that your HVAC system is neither oversized nor undersized, optimizing energy efficiency, comfort, and longevity.
Whether you’re installing a new system or replacing an existing one, understanding the HVAC load calculation process is crucial to making an informed decision.
What Is a Manual J Calculation?
The Manual J HVAC calculation is a detailed method used to calculate the heating and cooling loads required to maintain a comfortable temperature in a building.
Developed by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA), Manual J is considered the gold standard for sizing HVAC systems.
The calculation takes into account a variety of factors, including the size of the building, insulation levels, window types, air leakage, and external climate conditions.
Using this information, it determines the exact capacity needed to heat or cool the space without wasting energy.
This method is far more accurate than simple estimation techniques, like the rule-of-thumb sizing, and ensures the HVAC system is appropriately matched to your home or building.
What Inputs Are Used in Manual J?
A Manual J HVAC calculation requires detailed input data about the building to ensure the proper sizing of your system. The main inputs include:
- Construction Details: This includes the size of the building, the number of rooms, ceiling height, insulation quality, and types of materials used in walls, floors, and roofs.
- Occupancy: The number of people living or working in the space can affect the internal heat load. More people generally mean more heat generation, which must be accounted for in the calculation.
- Climate Data: Manual J takes into account the external climate conditions, including temperature extremes (both summer and winter), humidity levels, and the geographical location of the building. These factors influence the system’s heating and cooling demands.
- Window Types and Sizes: The type of windows and their total surface area plays a significant role in heat gain and loss. Double-pane windows, for example, offer better insulation than single-pane windows.
- Air Leakage: The presence of air leaks around doors, windows, and other openings can increase the heating and cooling load as they allow air from outside to infiltrate the home.
DIY vs Professional Manual J
While it may be tempting to attempt a Manual J HVAC calculation yourself, it’s important to know when it’s acceptable to go the DIY route and when it’s best to hire a professional.
When DIY Is Okay
- Simple Homes: If you have a basic home with typical insulation and standard windows, performing a Manual J calculation using online tools can be relatively straightforward.
- General Understanding: DIY calculations can be helpful to get a general idea of the HVAC size you need before discussing options with a professional.
When to Hire a Pro
- Complex Buildings: If your home has complex features, such as multiple floors, vaulted ceilings, large glass areas, or non-standard construction, hiring a professional is recommended.
- Accurate Results: A professional will ensure that all inputs are factored in accurately and perform the calculations properly. This is particularly important for homes in areas with extreme temperatures or unusual design features.
- Energy Efficiency: A professional can also advise you on how to improve insulation, air sealing, or other aspects of the home to improve energy efficiency and reduce overall heating and cooling costs.
Manual J vs Rule-of-Thumb Sizing
Many people are familiar with the “rule-of-thumb” method for sizing HVAC systems, which typically involves using square footage to estimate system size.
However, this method is far less accurate than a Manual J HVAC calculation, which considers a wide range of factors that affect the heating and cooling load.
| Factor | Manual J Calculation | Rule-of-Thumb Sizing |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Highly accurate, based on detailed building data. | Rough estimate, based on square footage alone. |
| Climate Consideration | Takes climate and external factors into account. | Ignores climate factors or uses simple adjustments. |
| Energy Efficiency | Optimizes for efficiency, avoiding oversized/undersized systems. | Often leads to oversized systems, wasting energy. |
| Complex Homes | Suitable for complex homes with custom features. | Does not account for complex layouts. |
| Cost | More expensive, requires professional input. | Free, but often inaccurate or inefficient. |
A Manual J HVAC calculation is essential for properly sizing your heating and cooling system. It ensures that your system runs efficiently, maintains comfort, and lasts longer.
While HVAC load calculation can be done manually or with tools, hiring a professional for more complex situations can ensure precise results and energy savings.
Whether you’re a DIY planner or hiring an expert, understanding the importance of the Manual J calculation helps you make the best decision for your HVAC system.
HVAC Sizing by Square Footage
When it comes to selecting the right HVAC size by square footage, many homeowners rely on general guidelines or charts that estimate the ideal HVAC system size based on the size of their home.
While these charts can provide a rough estimate, HVAC sizing per square foot should be treated as just one part of the overall sizing process.
A proper HVAC sizing calculation should consider many more factors that influence heating and cooling needs.
HVAC Size Chart by Home Size
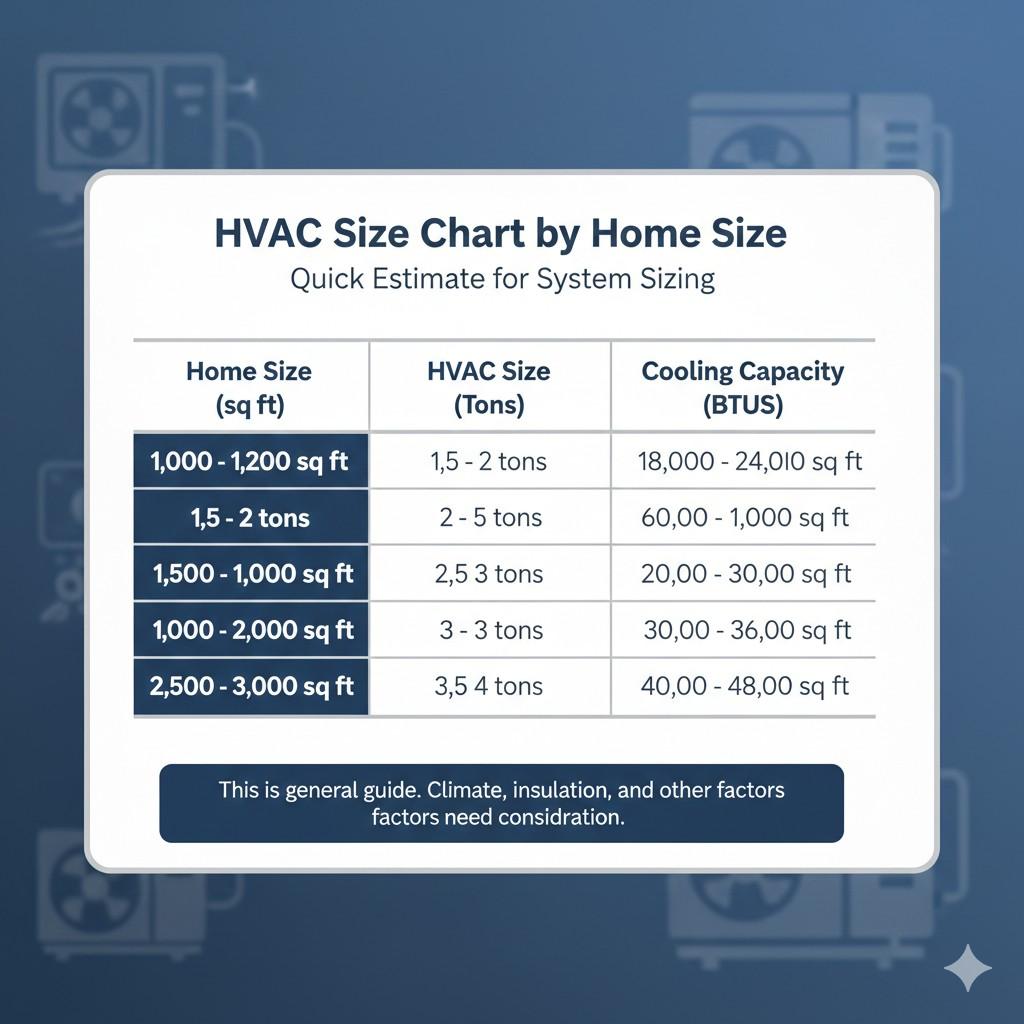
Here’s a general HVAC size chart by square footage to give you an initial estimate of the system you may need. Keep in mind that this is just a starting point. Climate, insulation, and other factors will still need to be considered.
| Home Size (sq ft) | HVAC Size (Tons) | Cooling Capacity (BTUs) |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 – 1,200 sq ft | 1.5 – 2 tons | 18,000 – 24,000 BTUs |
| 1,200 – 1,500 sq ft | 2 – 2.5 tons | 24,000 – 30,000 BTUs |
| 1,500 – 2,000 sq ft | 2.5 – 3 tons | 30,000 – 36,000 BTUs |
| 2,000 – 2,500 sq ft | 3 – 3.5 tons | 36,000 – 42,000 BTUs |
| 2,500 – 3,000 sq ft | 3.5 – 4 tons | 42,000 – 48,000 BTUs |
Disclaimer: These values are based on a standard home with average insulation and typical climate conditions.
For the most accurate results, HVAC sizing must consider specific variables such as insulation, window types, ceiling height, and climate zone.
Why Square Footage Charts Are Not Enough
While the square footage vs HVAC size chart provides a rough estimate, it’s important to understand the risks of oversimplification. Using only the square footage of your home to size your HVAC system can lead to common problems such as:
- Oversized Systems: An oversized system can lead to short cycling, where the system turns on and off frequently. This wastes energy, reduces comfort, and shortens the system’s lifespan.
- Undersized Systems: A system that is too small will struggle to maintain the desired temperature, resulting in constant operation, inconsistent temperatures, and higher wear and tear on the unit.
Callout Warning Box:
IMPORTANT: Relying solely on square footage for HVAC sizing can lead to inefficient performance and higher energy bills.
Always consider other critical factors such as climate, insulation, and window quality when determining the right system size.
While HVAC sizing per square foot can provide a quick reference, it is only one piece of the puzzle. To ensure your HVAC system operates efficiently, consult a professional for a full HVAC sizing calculation that takes into account your home’s unique characteristics.
Sizing Different Types of HVAC Systems
Different types of HVAC systems have different sizing requirements based on how they function. Below, we’ll discuss how to size systems like furnaces, air conditioners, heat pumps, and ductless mini-splits. Each system type has unique considerations, and understanding these is key to making the right choice for your home.
Furnace Sizing
Furnaces can be gas-powered or electric-powered, and proper sizing is essential for efficiency and performance.
- Gas vs Electric Furnaces: Gas furnaces require a larger capacity to efficiently heat larger homes, while electric furnaces are typically used for smaller homes or as supplemental heat. The efficiency of a gas furnace is measured in AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency), and the higher the AFUE, the better.
- Sizing Considerations: Furnace sizing depends on the heating load of your home, which is determined by factors like square footage, insulation, and ceiling height. A Manual J calculation is crucial to properly size a furnace for your home.
Tip: Always choose a furnace with a high AFUE rating to ensure energy savings and efficiency.
Central Air Conditioner Sizing
Central air conditioners are sized based on their SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), which determines how efficiently the unit cools your home.
- SEER Impact: The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the system. A higher SEER rating allows the system to cool the same amount of space using less energy, which reduces operational costs.
- Sizing Considerations: Air conditioner sizing depends on the cooling load of your home, which includes the amount of heat your home absorbs from the sun, the insulation level, and your home’s overall size. Larger homes and those in hotter climates require higher cooling capacity.
Tip: Choose an air conditioner with a SEER of 14 or higher for optimal energy efficiency.
Heat Pump Sizing
A heat pump works by transferring heat from outside to inside in winter and vice versa in summer. These systems are ideal for moderate climates, though cold climate considerations are necessary.
- Cold Climate Considerations: In colder climates, heat pumps might require supplemental heating, such as electric heat strips, as their efficiency drops when the outside temperature falls below freezing.
- Sizing Considerations: Heat pumps require a balance between heating and cooling load, with proper sizing ensuring that the system provides sufficient comfort in both winter and summer.
Tip: Consider a dual-source heat pump (combining a heat pump with a furnace) for better efficiency in colder regions.
Ductless Mini-Split Sizing
Ductless mini-splits are ideal for homes without existing ductwork or those that require room-by-room heating and cooling.
- Room-by-Room Sizing: With ductless systems, each unit is typically sized for one room or zone. Proper sizing depends on room size, insulation, window type, and other factors specific to the room.
- Multiple Units: If your home requires multiple zones, multiple ductless units may be needed to maintain comfort throughout the entire space.
Tip: Ductless systems are best for homes with diverse heating/cooling needs in separate rooms.
Comparison Table: System Type vs Sizing Considerations
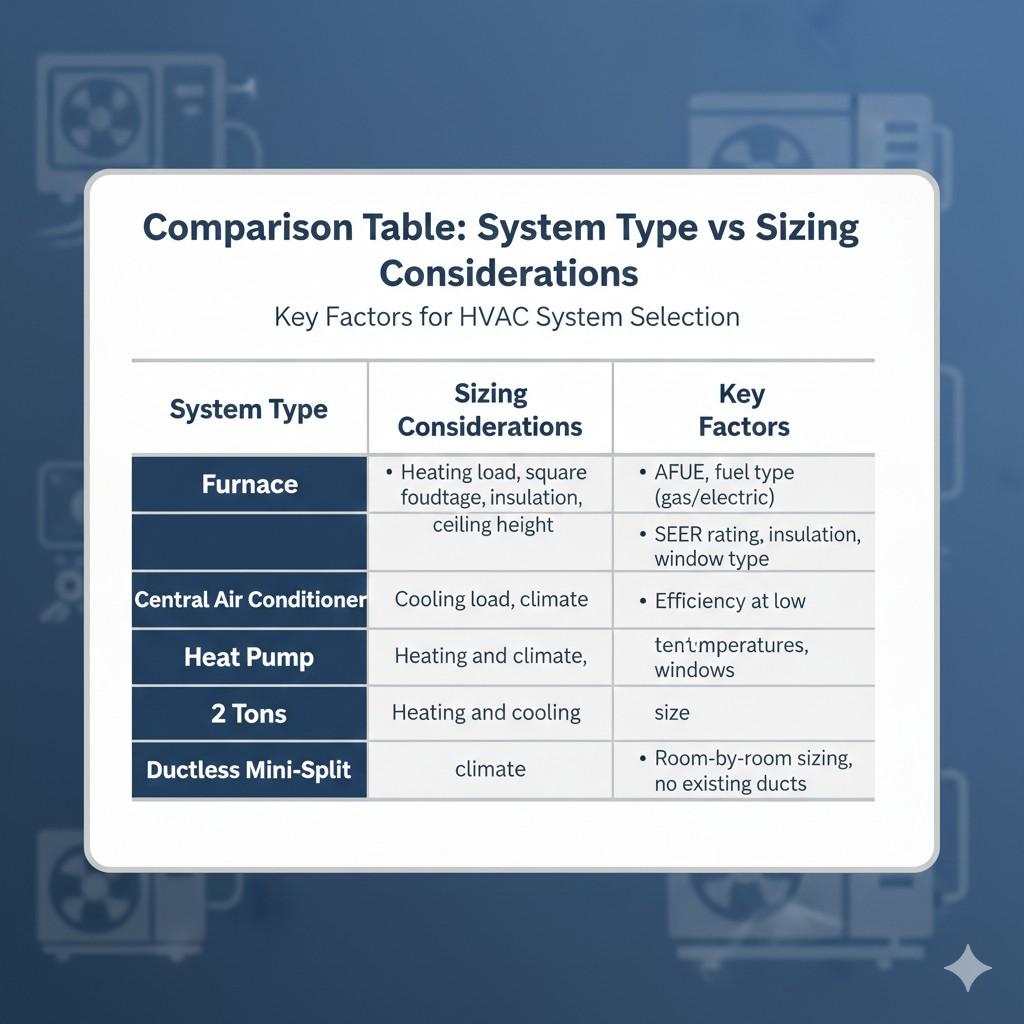
| System Type | Sizing Considerations | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace | Heating load, square footage, insulation, ceiling height | AFUE, fuel type (gas/electric) |
| Central Air Conditioner | Cooling load, climate, square footage | SEER rating, insulation, window type |
| Heat Pump | Heating and cooling load, climate | Efficiency at low temperatures, size |
| Ductless Mini-Split | Room size, insulation, windows, zoning | Room-by-room sizing, no existing ducts |
Sizing your HVAC system correctly is crucial to ensuring that it operates efficiently and keeps your home comfortable year-round.
Whether you’re selecting a furnace, air conditioner, heat pump, or ductless mini-split, each system has its own specific sizing requirements that depend on factors such as climate, insulation, and home layout.
Always work with a professional to ensure your system is properly sized for optimal performance and energy savings.
Common HVAC Sizing Mistakes to Avoid
Proper HVAC sizing is crucial for efficiency, comfort, and cost savings. Unfortunately, many homeowners make sizing mistakes that lead to inefficiencies, higher energy bills, and even system failure.
By understanding the most common HVAC sizing mistakes, you can ensure your system is properly sized for your space, preventing costly errors and problems down the road.
Relying Only on Square Footage
One of the most common HVAC sizing mistakes is relying solely on square footage to determine system size. While square footage is a factor, it’s not the only one.
Homes with high ceilings, multiple levels, or poor insulation may require larger systems, while homes with proper insulation or shaded areas might need smaller systems.
HVAC sizing per square foot gives a rough estimate but fails to account for several important variables.
- Consequence: An oversized or undersized system that leads to inefficiency, discomfort, and higher energy bills.
Copying Neighbor’s System Size
Many homeowners make the mistake of copying the HVAC system size of a neighbor’s home, assuming their system will work similarly.
However, every home is unique, with different layouts, insulation levels, and climate conditions. What works for one home may not work for yours.
- Consequence: Poor system performance and potential breakdowns due to incorrect sizing based on another home’s needs.
Ignoring Insulation and Climate
Neglecting to consider your home’s insulation and the climate you live in is another critical mistake. Homes in colder climates need larger heating systems, while homes in warmer areas need systems that handle heat gain effectively. Additionally, homes with poor insulation will require a larger system to compensate for energy loss.
- Consequence: Energy inefficiency, inconsistent temperatures, and potential system failure due to improper sizing for climate and insulation conditions.
Skipping Professional Load Calculation
A professional HVAC load calculation is the most accurate method for determining your system’s size. Skipping this important step can result in poorly sized systems.
A Manual J calculation considers all factors, including insulation, climate, and air leakage, to provide a precise HVAC size that suits your needs.
- Consequence: Short cycling, frequent breakdowns, increased energy bills, and a system that doesn’t perform as expected.
Mistakes vs Consequences Table
| Mistake | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Relying only on square footage | Oversized or undersized system, leading to inefficiency and discomfort. |
| Copying neighbor’s system size | System may not be appropriately sized for your unique home, causing issues. |
| Ignoring insulation and climate | Increased energy costs, inconsistent temperatures, and system inefficiency. |
| Skipping professional load calculation | Poor system performance, short cycling, and potentially higher repair costs. |
Avoiding these common HVAC sizing mistakes is essential for selecting the right system for your home. Always consider factors like insulation, climate, and a professional load calculation to ensure you make the best decision for comfort and energy efficiency.
A properly sized HVAC system will not only save you money on energy bills but will also extend the lifespan of your equipment and provide consistent comfort throughout your home.
Cost Impact of Proper HVAC Sizing
Proper HVAC sizing not only ensures comfort and efficiency but also has a significant impact on your financial decisions.
Choosing the correct system size can affect installation costs, long-term energy bills, and maintenance expenses. In this section, we’ll explore how energy-efficient HVAC sizing can save you money in both the short and long term.
Installation Cost Differences
The HVAC sizing cost plays a crucial role in determining the upfront installation expenses. An oversized HVAC system often costs more to install because it requires more materials, such as larger ducts or more powerful equipment.
On the other hand, an undersized HVAC system may require additional modifications to ensure proper performance, leading to higher labor costs.
- Oversized system installation costs: Higher equipment and labor costs.
- Undersized system installation costs: Potential for extra installation work to correct sizing issues.
Cost Comparison:
- Oversized System: Higher installation cost due to increased equipment size and complexity.
- Undersized System: Higher labor costs due to needed adjustments for system efficiency.
Energy Bills and Long-Term Savings
Proper HVAC sizing significantly influences your energy bills. Energy-efficient HVAC sizing ensures that your system runs at optimal capacity without overworking, reducing energy consumption.
An oversized system wastes energy by turning on and off frequently, while an undersized system works constantly, driving up your energy costs.
- Oversized HVAC system: Leads to higher energy consumption due to short cycling.
- Undersized HVAC system: Causes constant running, increasing energy use and costs.
Energy Savings:
- Properly sized systems use energy efficiently, resulting in lower monthly energy bills.
- Oversized or undersized systems increase operational costs due to inefficiency.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
An improperly sized HVAC system can lead to increased maintenance and repair costs. An oversized HVAC system undergoes unnecessary cycling, which puts more stress on its components, leading to more frequent repairs.
An undersized system works harder to meet demand, causing wear and tear over time, ultimately resulting in costly repairs and early system failure.
- Oversized system maintenance costs: Higher due to more frequent repairs and parts replacement.
- Undersized system maintenance costs: Increased wear and tear from constant operation, leading to early system breakdowns.
Cost Comparison:
- Properly sized system: Balanced operation, leading to lower repair and maintenance costs.
- Oversized or undersized system: Higher repair and maintenance costs due to system inefficiency.
Correct Sizing vs Incorrect Sizing Costs
| Cost Factor | Correct Sizing | Incorrect Sizing (Oversized/Undersized) |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Costs | Standard installation cost | Higher due to equipment or labor adjustments |
| Energy Bills | Lower energy costs due to efficient operation | Higher energy costs due to inefficiency |
| Maintenance and Repairs | Reduced costs with optimal operation | Increased due to stress on system components |
The cost of HVAC sizing extends far beyond the initial installation. Energy-efficient HVAC sizing ensures long-term savings on your energy bills, reduces repair and maintenance costs, and prevents the financial burden of replacing equipment too soon.
By selecting the right size HVAC system for your home, you’ll enjoy a more efficient, cost-effective solution that provides comfort and savings for years to come.
When to Call a Professional for HVAC Sizing
Proper HVAC sizing is crucial for efficiency, comfort, and long-term savings. While DIY tools can provide rough estimates, there are several situations where it’s best to seek professional HVAC sizing.
Inaccurate sizing can lead to inefficiency, higher energy bills, and even system breakdowns, making expert help invaluable.
Signs You Need Expert Help
- Unbalanced Temperature Distribution: If certain rooms are consistently too hot or too cold, it may indicate your HVAC system is improperly sized for your space.
- Frequent System Cycling: If your system constantly turns on and off (short cycling), it’s often a sign of an oversized system that is inefficient.
- Higher Energy Bills: Significant spikes in your energy costs, especially if there’s no change in your usage, could indicate an oversized or undersized system.
- System Age or Upgrades: If you’re upgrading an old system or installing a new one in a remodeled space, a professional HVAC sizing service ensures everything is properly calibrated for the new setup.
What a Professional Will Evaluate
A professional HVAC technician will perform a comprehensive HVAC sizing calculation that includes evaluating the following:
- Home Size and Layout: The technician will measure the total square footage and consider room layouts, ceiling height, and the number of floors.
- Insulation and Windows: They’ll assess the home’s insulation, window types, and how these affect the home’s heating and cooling load.
- Climate and Exposure: The technician will factor in your local climate and any environmental conditions (e.g., direct sunlight, humidity) that impact system performance.
- Energy Efficiency: A professional will also ensure that your system is energy-efficient, choosing the best system for your home’s specific needs.
Questions to Ask Contractors
When hiring an HVAC professional for sizing, ask the following questions:
- “Do you perform Manual J load calculations?” (This ensures accurate sizing.)
- “How do you factor in insulation and climate conditions?”
- “Can you provide a detailed estimate of installation costs?”
- “What is the recommended system size for my specific needs?”
Checklist for Professional HVAC Sizing
- Is your HVAC system inefficient or unbalanced?
- Are you upgrading or installing a new system?
- Do you need to ensure energy efficiency?
- Is your system cycling too frequently?
- Are your energy bills unusually high?
If you’re facing any of the above signs or want to ensure your HVAC system is properly sized, it’s time to call a professional.
Professional HVAC sizing ensures that your system runs at peak efficiency, saves on energy bills, and prevents unnecessary repairs.
Trusting a licensed expert to handle your HVAC sizing service will provide you with peace of mind and long-term savings. Don’t wait—schedule your HVAC sizing service today!
See also Heating System Installation
Frequently Asked Questions About HVAC System Sizing
Sizing your HVAC system correctly is crucial for efficiency, comfort, and long-term savings. Here are some of the most commonly asked questions about HVAC sizing and their answers.
What size HVAC system do I need for my home?
The size of the HVAC system you need depends on several factors, including your home’s square footage, insulation, climate, and layout. Typically, systems are measured in BTUs (for heating and cooling) or tons (for cooling). A general rule is that you need about 1 ton per 600-800 sq ft of living space, but it’s best to have a professional HVAC sizing calculation, such as a Manual J load calculation, to ensure proper sizing.
Is it better to oversize or undersize HVAC?
Neither oversizing nor undersizing your HVAC system is ideal. Oversized HVAC systems lead to short cycling, which wastes energy and reduces the lifespan of the equipment. Undersized systems, on the other hand, will struggle to maintain your desired temperature, run constantly, and wear out prematurely. A properly sized system will operate efficiently, ensuring comfort without overburdening your energy bills.
Can I size my HVAC system myself?
While there are online calculators that can help you estimate your HVAC needs, sizing a system yourself is generally not recommended unless you have extensive experience. Proper sizing requires a detailed HVAC sizing calculation that factors in elements like insulation, windows, air leakage, and local climate conditions. It’s always best to consult a professional who can perform a Manual J calculation to ensure your system is correctly sized.
Does HVAC size affect energy efficiency?
Yes, HVAC size has a significant impact on energy efficiency. An oversized system will waste energy by cycling on and off too frequently, leading to higher electricity bills. An undersized system will consume more energy trying to meet the heating or cooling demand, resulting in constant running. Proper sizing ensures that your system runs efficiently, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility costs.
Is Manual J required for HVAC sizing?
While Manual J is not legally required, it is the gold standard for HVAC sizing. It provides a precise calculation based on your home’s unique characteristics, such as square footage, insulation, and climate. Using Manual J ensures that your system is appropriately sized for your space, leading to better performance, energy efficiency, and comfort.
Final Thoughts on How to Size a Heating and Air Conditioning System
Choosing the right HVAC system for your home requires more than just knowing your square footage. Proper HVAC sizing involves considering many factors such as insulation, climate, and energy efficiency. Accurate sizing ensures that your system runs efficiently, providing comfort without wasting energy or incurring unnecessary costs.
Key Takeaways
- Accurate sizing saves money: Properly sized systems are more energy-efficient and reduce long-term operational costs.
- Manual J is the gold standard: For the most accurate sizing, Manual J calculations take all variables into account.
- Climate and insulation matter: Understanding your local climate and the insulation of your home is key to choosing the right system size.
- Professional sizing ensures comfort: Hiring a professional to perform a detailed sizing calculation ensures that your HVAC system provides the comfort and efficiency you need.
Summary Bullets
- Correct HVAC sizing improves comfort, energy efficiency, and system longevity.
- Manual J sizing is recommended for precise calculations.
- Oversizing or undersizing an HVAC system can lead to increased costs and reduced efficiency.
- Always consider insulation, climate, and system load when sizing your HVAC.
Quick Reference Table: Home Type vs Recommended Approach
| Home Type | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|
| Small Homes (1,000 – 1,500 sq ft) | Perform Manual J sizing for accurate load calculation |
| Medium Homes (1,500 – 2,500 sq ft) | Consider climate, insulation, and layout; consult an expert for HVAC sizing |
| Large Homes (2,500+ sq ft) | Always hire a professional for a detailed HVAC sizing calculation |
| Homes with Poor Insulation | Account for additional energy loss; use Manual J for better accuracy |
Proper HVAC sizing is essential for ensuring comfort, reducing energy bills, and prolonging the lifespan of your system. By using a professional HVAC sizing service and taking into account key factors like insulation, climate, and system load, you can ensure that your system operates efficiently.
For the best results, always use Manual J calculations or consult an expert to avoid costly mistakes and enjoy long-term comfort. Ready to get started? Contact a professional today for your HVAC sizing needs!
See also HVAC Tune-Up Checklist

